-
01/17/2026
- 0 Comment
What is DB-Type Linear Guide Structure?
In CNC router and precision automation design, selecting the right linear guide for CNC is crucial for performance, accuracy, and reliability. Among the many CNC rails available, the DB (Back-to-Back) type linear guide has proven to be an excellent solution for heavy-duty linear rail applications and high-stability scenarios.
1. What is DB Structure?
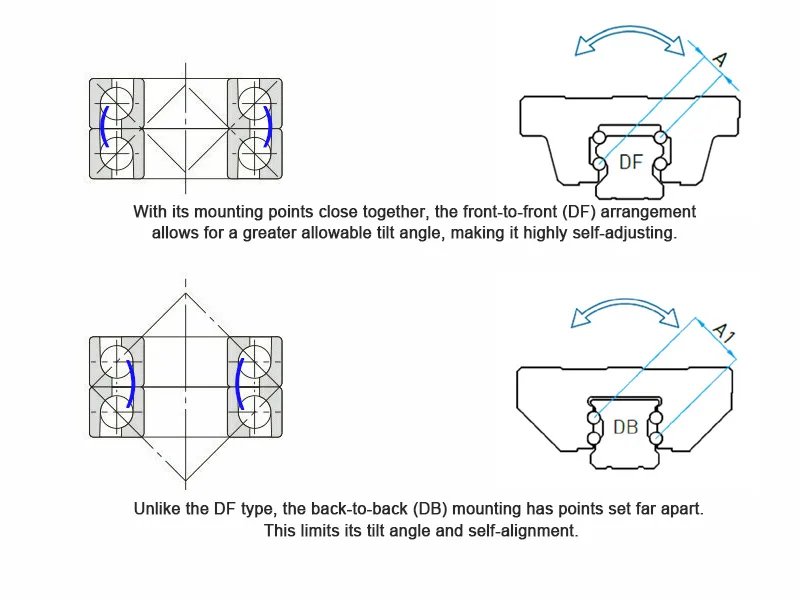
The DB structure, short for Back-to-Back ball arrangement, is a CNC linear rail block design that uses balls instead of rollers. In this design, the rows of rolling elements are oriented outward, in contrast to the DF (Face-to-Face) structure, where the balls face inward.
Physically, the DB structure distributes contact points farther apart, effectively increasing the lever arm for resisting tilting or overturning forces.
- DF = Face-to-Face → smooth motion, suitable for standard linear rails CNC and high-speed, light-load axes.
- DB = Back-to-Back → high stability and load-bearing capacity, capable of replacing roller guides in certain heavy-duty linear rail applications, providing a cost-effective solution while retaining the advantages of ball-type linear guides.
2.Core Advantages & Application of DB Structure
| DB Structure Advantage | Typical Applications | Unsuitable Scenarios / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| High load capacity in vertical direction | Z-axis lifting modules, vertical machining centers, automated loading & unloading systems | Not ideal for ultra-high-speed, light-load axes; may result in unnecessary rigidity and cost |
| Excellent anti-overturning and moment resistance | Cantilever structures, long-stroke single-side supported platforms, off-center load systems | Higher requirements for mounting surface accuracy; poor base flatness may reduce performance |
| High running stability, vibration suppression | High-frequency start-stop equipment, precision inspection systems, semiconductor equipment | DF structure is more suitable when extreme speed and ultra-low friction are required |
| Can replace roller guides in certain applications | Medium-to-high load automation lines, cost-sensitive heavy-duty equipment | Not suitable for extremely heavy loads or applications requiring ultra-high rigidity (e.g. spindle axes) |
| Strong adaptability to eccentric loads | Eccentrically mounted fixtures, asymmetrical platforms, multi-station mechanisms | Long-term extreme eccentric loads require life calculation and safety factor verification |
| High rigidity, suitable for heavy loads | Heavy-cutting CNC machines, industrial testing platforms, large automation equipment | More sensitive to mounting parallelism and bolt tightening torque; proper installation is critical |
| Better cost-performance than roller guide solutions | Mass equipment production, system integration projects | May be over-engineered if system accuracy and rigidity requirements are low |
3.Physics Behind DB Stability in CNC Rails
Mechanically, stability comes from resisting torque (moment):
M=F×dM = F \times dM=F×d
F = external load
d = distance from force application to the guide’s central axis
DF linear rails CNC have closer contact points (shorter d), so the resisting moment is smaller. They are suitable for high-speed, light-load XY axes.
DB CNC linear guides have contact points spread outward (longer d), creating a stronger moment against tilt or torsion:
MDB=F×dDB(dDB>dDF)
This makes DB guides ideal for Z-axis CNC router linear guides and cantilevered structures.
4.When Should DB-Type Linear Guides Not Be Used?
Although DB (Back-to-Back) linear guides offer high stability, excellent load capacity, and the ability to replace some roller guides in heavy-duty applications, there are specific situations where they are not suitable:
Ultra-high-speed, light-load applications
- DB guides have higher contact angles and slightly higher friction than DF guides, which can limit maximum speed.
- For fast, low-load XY axes or high-speed CNC routers, a DF (Face-to-Face) structure is often better.
Extremely heavy spindle or cutting loads
- In cases where maximum rigidity is required, such as heavy-cutting CNC spindles, traditional roller guides may still outperform DB guides.
Poorly prepared or imprecise installation surfaces
- DB guides rely on proper base flatness and parallelism to achieve full load distribution.
- Uneven mounting surfaces can reduce accuracy, cause uneven wear, or shorten service life.
Applications where cost-effectiveness is not a concern
- If the system already uses roller guides and high rigidity is essential, replacing them with DB guides might be unnecessary.
5. DF vs DB CNC Linear Guides: Quick Comparison
| Feature | DF (Face-to-Face) | DB (Back-to-Back) |
|---|---|---|
| Load capacity | Medium | High (heavy-duty linear rail) |
| Anti-tilt / anti-torque | Medium | High |
| Running stability | Smooth, high-speed | Very stable, anti-vibration |
| Best for | Horizontal, XY axes, high-speed | Vertical, Z-axis, heavy-duty, cantilevered CNC rails |
| Cost | Lower | Moderate (higher than DF, lower than roller guides) |
6.DTX-LG linear rail solution
DTX-LG offers a wide range of high-quality linear guides for CNC and heavy-duty applications:
DF (Face-to-Face) structure products:
- SG, SE, SM series – designed to replace Hiwin HG, EG, and MG series, offering smooth motion and high-speed performance for standard linear rails CNC applications.
DB (Back-to-Back) structure products:
- SD series – engineered for high stability and load-bearing capacity, capable of replacing Bosch Rexroth BSCL series, ideal for vertical axes, cantilevered structures, and heavy-duty CNC rails.

DTX-LG is a professional manufacturer of precision linear guides, offering high interchangeability, customized solutions, and reliable supply for industrial automation, CNC machinery, and heavy-duty applications.
For more information or technical support, please contact DTX-LG team. We are ready to assist you with product selection, customization, and integration into your CNC or automation projects.