-
12/12/2025
- 0 Comment
Hydrostatic Box Ways vs Linear Guideways
What’s the difference?
Both Linear Guideways (ball linear guide/roller linear guide/curve curved linear rail) and Hydrostatic Guideways are considered core linear motion system in machine tools and mechanical systems.Their primary function is to constrain the trajectory of a moving element, ensuring its movement is highly accurate and stable along a predefined straight line. Concurrently, they are designed to support the applied load and transmit the driving forces.
What are Hydrostatic Box Ways?
Hydrostatic Box Ways operate on the same principle as hydrostatic bearings. Lubricating oil, maintained at a specific pressure, is introduced through a restrictor (throttle) into recesses (pockets/chambers) located on the guideway surface. This creates a load-bearing oil film, ensuring that the guideway surfaces are separated and operate strictly under conditions of pure liquid friction.
Hydrostatic Box Ways Advantages
Ultra-High Precision and Stability: The absence of mechanical contact eliminates wear. The error-averaging effect of the oil film compensates for manufacturing errors in the guideways, allowing positioning accuracy to reach the sub-micron level.
Exceptional Load Capacity and Stiffness: The combination of a closed box-way structure and a high-pressure oil film allows the system to withstand large cutting forces and overturning moments, making it ideal for heavy-duty work piece machining.
Superior Motion Smoothness: Extremely low friction eliminates low-speed stick-slip (crawling), providing superior dynamic response. This makes it suitable for high-precision contouring (interpolation motion) of complex surfaces.
Excellent Damping and Thermal Management: The oil film provides damping to suppress cutting vibrations. Simultaneously, it carries away friction heat, minimizing the impact of thermal deformation on precision.
What is Linear Guideway?
A linear guideway (also known as linear guide rail, linear slide rail, or in some regions, linear rails) is used in applications requiring high-precision or high-speed linear reciprocating motion. It is designed to handle significant torque and can achieve highly accurate linear movement under heavy load conditions.
Classification of Linear Guides
- Ball linear guide
- Roller linear guide
- Low profile linear rail
- Miniature linear guide
- Curved linear rail system
- V lienar rails

BALL LINEAR GUIDE
Interchangeable with hiwin's HG series,suitable for CNC machineries
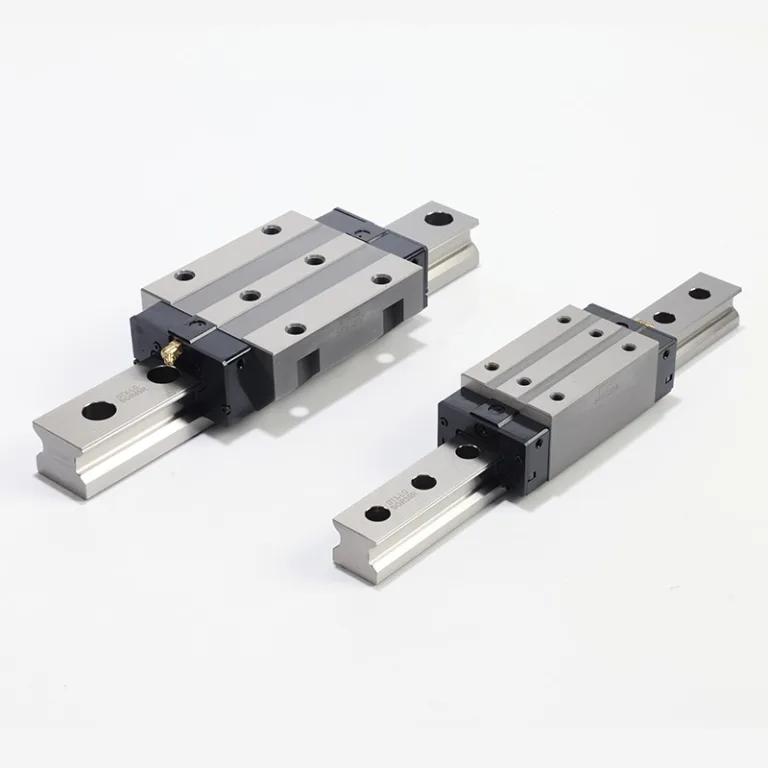

ROLLER LINEAR GUIDE
Interchangeable with hiwin's RG series,suitable for high rigidity applications
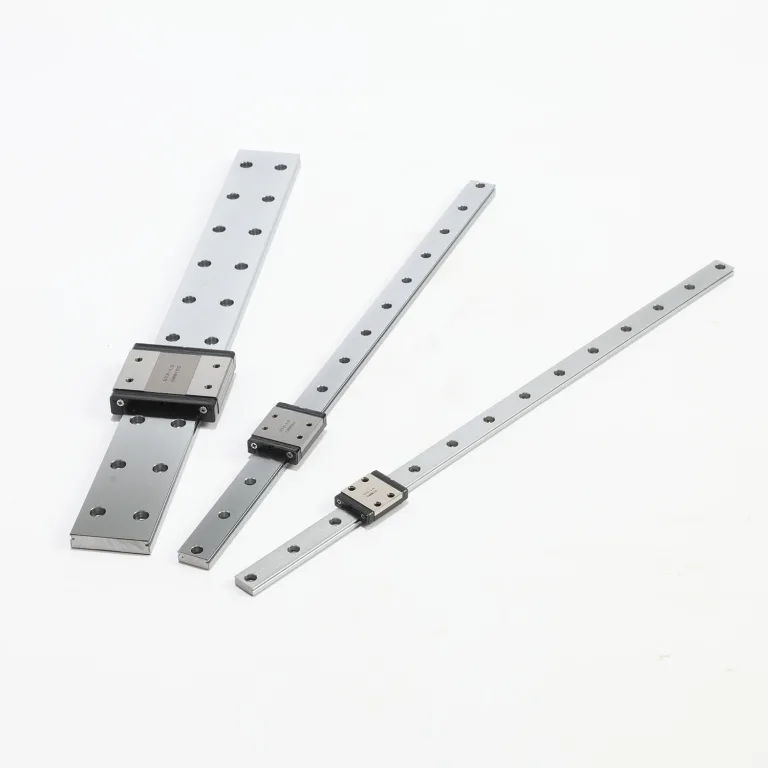

MINIATURE LINEAR GUIDE
Interchangeable with hiwin's MG series,suitable for medical devices and semiconductor equipment

LOW PROFILE LINEAR GUIDE
Interchangeable with hiwin's EG series,suitable for automation industries
Linear Guideways Advantages
High Precision: Features low friction and eliminates stick-slip (low-speed crawling). When preloaded, the resulting repeatability and positioning accuracy can reach the micron level.
High Load Capacity and Rigidity (Stiffness): Capable of handling loads from multiple directions and resisting overturning moments. Provides excellent structural rigidity.
Easy Installation: Features a standardized design with good interchangeability, eliminating the need for complex adjustments or lengthy setup.
Wide Applicability: Available in various sizes/specifications and precision grades. Can be easily integrated in a modular fashion with components like ball screws or linear motor modules.
Low Maintenance: Incorporates a built-in self-lubricating structure, resulting in a long service life and lower long-term maintenance costs.
High Speed Capability: Suitable for high-speed reciprocating movement with excellent dynamic response characteristics.
Are They Substitutable?
Linear guides (roller type/ ball type /curved linear rail systems) and hydrostatic guideways CANNOT be freely substituted for each other. They can only be swapped in a few low-demand situations. In most industrial applications, you must choose based on the actual requirements, because the two systems differ greatly in working principle, supporting components, cost, and performance.
4 key reasons why they are not interchangeable
- A hydrostatic guideway relies entirely on a dedicated oil supply system, while a linear guideway has no oil-film compensation capability. In other words: A hydrostatic guide requires an oil station and piping to generate the supporting oil film—without oil, it simply cannot operate.
A linear guide does not need an oil station, but it also lacks oil-film compensation, so its load capacity and stability are inherently limited. - In ultra-precision applications, the accuracy and stability of linear guideways cannot match those of hydrostatic guideways.Put simply: If you need nanometer or sub-micron accuracy, linear guides cannot achieve the “self-averaging” and “more load, more stability” behavior that hydrostatic oil films naturally provide.
- Hydrostatic guideways are expensive and maintenance-intensive, while linear guideways cannot handle heavy-duty cutting vibrations.Hydrostatic systems are costly and complex; linear guides are affordable and easy to maintain—but in heavy-cutting or high-vibration environments, linear guides cannot replace the high stiffness and damping of hydrostatic systems.
- Hydrostatic guideways are sensitive to contamination and unsuitable for harsh environments; linear guideways are not ideal for ultra-clean or vacuum conditions.A hydrostatic guide’s oil circuit is easily affected by contamination.
Linear guides contain rolling elements that generate wear particles, which can contaminate cleanrooms and are unsuitable for vacuum applications.
Overview of Key Performance Differences
| Parameter | Hydrostatic Guideway (Liquid / Gas) | Linear Guideway |
| Positioning / Repeatability | Achievable in sub-micron to nanometer range, straightness ≤0.1 μm/250 mm, error self-compensation effect | Precision grade ±0.5–±1 μm, ultra-precision grade up to ±0.2 μm, depends on preload and manufacturing accuracy |
| Rigidity | High | Moderate |
| Long-term Stability | Contact-free, no wear, precision almost unchanged, theoretically unlimited lifespan | Rolling elements and guideway suffer fatigue wear, long-term precision gradually decreases |
| Low-Speed Smoothness | Extremely low friction coefficient (~0.0001–0.001), no stick-slip, very smooth startup | Friction coefficient relatively higher (~0.001–0.005), may exhibit stick-slip at low speed |
| Vibration Damping & Error Compensation | Strong oil-film damping, absorbs vibration, averages out guideway manufacturing errors | Weak vibration damping, relies on preload and auxiliary damping optimization |
World-leading suppliers
globally renowned linear guides manufacturer
- THK (Japan)
- IKO (Japan)
- Bosch Rexroth (Germany)
- Schneeberger (Germany)
- HIWIN (Taiwan)
- DTX-LG (China) : wholesale linear guide rail and carriage
globally renowned Hydrostatic Box Ways manufacturer
- ZOLLERN (Germany)
- HYPROSTATIK (Germany)