
-
01/20/2026
- 0 Comment
From Theory to Practice: Authoritative Guide to ISO 14728 Lifespan Calculation in Linear Guides
Ensuring Reliability and Long-Term Performance for Linear Motion Companies
Table of Contents
Background of Linear motion components
Linear guides are the backbone of modern precision machinery, ranging from CNC machines and robotics to automated production lines. For any linear motion company or industrial automation provider, ensuring linear guide reliability is crucial, as the lifespan of a linear guide directly affects equipment performance, maintenance costs, and operational safety.
Predicting the lifespan of linear guides is not trivial. Miscalculations can result in early wear, unexpected downtime, and costly replacements. This is why ISO 14728 is widely adopted by leading linear guide manufacturers. By following ISO 14728, linear rail companies can provide reliable, long-lasting products, while engineers can make informed decisions on guide selection, load capacity, and maintenance schedules.
What is ISO 14728 Standard?
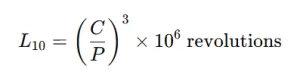
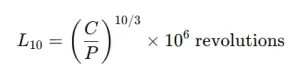
Theoretical Basis for Lifespan Calculation
Understanding the theory behind linear guide lifespan is critical for any linear guide manufacturer, system integrator, automated equipment factory…..
Dynamic vs static loads: Guides experience forces in multiple directions; differentiating constant and moving loads is essential.
Rolling element configuration: The number and arrangement of balls or rollers affect load distribution, friction, and lifespan.
Contact points: Multiple rolling elements ensure two or more points of contact, reducing stress per contact.
Friction and lubrication: Proper lubrication reduces friction, extending the linear motion system’s lifespan.
By applying these principles, linear motion companies can select suitable guide types, calculate expected L10 life, and ensure system reliability.
From Theory to Practice: Lifespan Calculation Workflow
Applying ISO 14728 in real-world linear motion systems requires a structured workflow. To illustrate, let’s consider a practical example using a DTX-LG linear guide model SGH65HA.
Step 1: Collect Operational Data
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum velocity (V) | 0.5 | m/sec |
| Acceleration (a) | 0.083 | m/sec² |
| Load coefficient (fw) | 1.4 | – |
| Stroke (S) | 28000 | mm |
| Cycle frequency (n) | 0.48 | 1/min |
| Number of sliders | 2 | – |
| Number of balls per slider | 5 | – |
This data reflects real operating conditions of a linear guide manufacturer’s product under typical CNC or automation workloads.
Step 2: Identify Load Conditions
| Load Type | Equivalent Load (N) |
|---|---|
| Acceleration | 45,336.25 |
| Constant velocity | 45,107.65 |
| Deceleration | 45,447.12 |
| Maximum slider load | 45,210.75 |
Other geometric parameters include slider center distances (Mc, G1, G2, G3) and guide rail distances (d1, e). These values allow linear rail companies and linear motion companies to calculate precise L10 lifespans, taking into account the real-world forces acting on each guide.
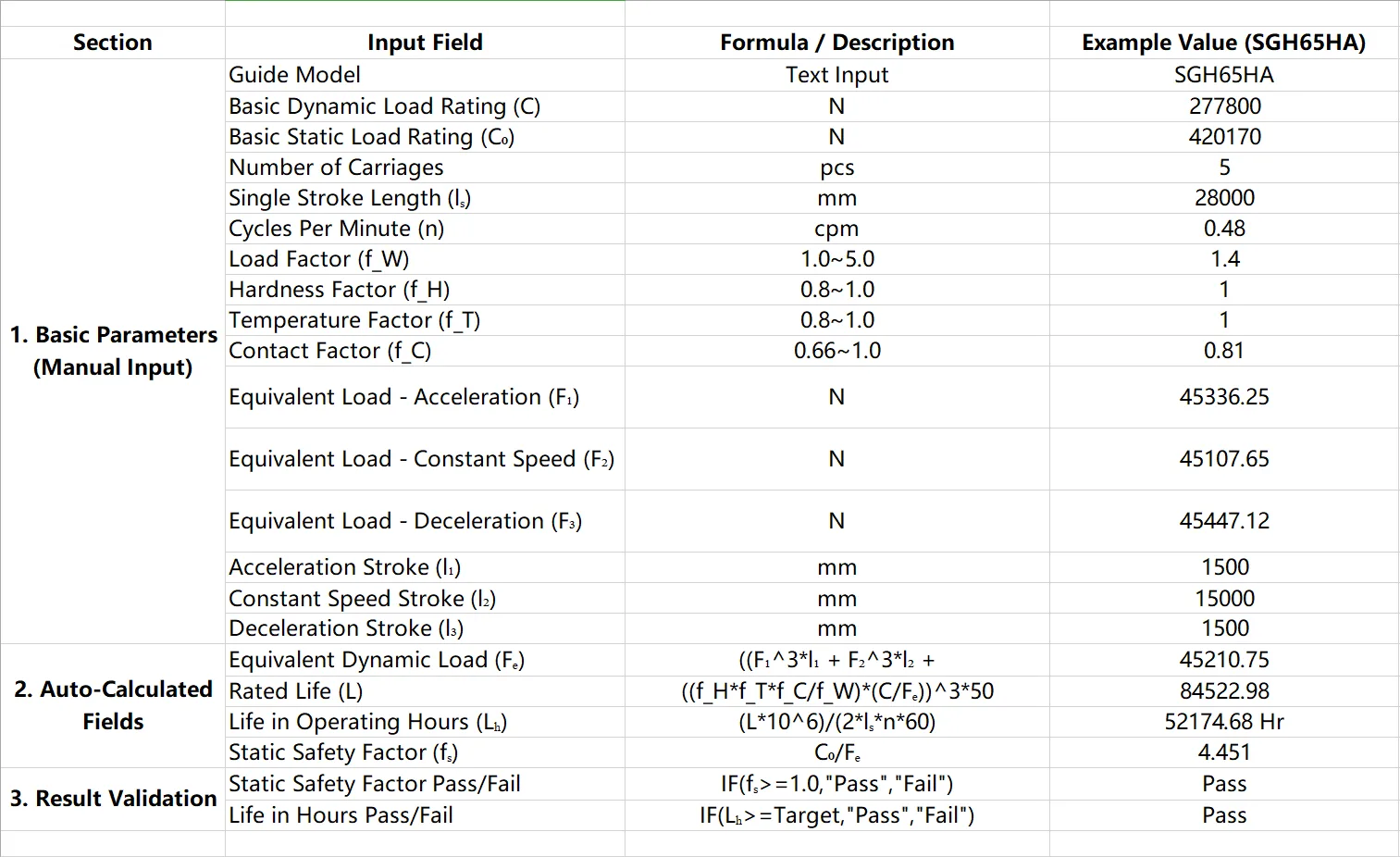
Step 3: Calculate L10 Lifespan
Using ISO 14728 formulas, the lifespan can be calculated in hours and travel distance. For this SGH65HA guide:
- Static safety factor: 4.451
- Calculated L10 life: 52,174.68 hours (~5.96 years continuous operation)
- Equivalent travel distance: 84,522.98 km
This demonstrates how a linear guide manufacturer can quantify reliability and provide clients with precise expectations of linear motion performance.
Step 4: Insights for Design Optimization
- Using multiple sliders and high-quality materials ensures lower stress per rolling element, increasing lifespan.
- Proper alignment and lubrication reduce wear, even under long-distance travel and repeated acceleration/deceleration cycles.
- Data-driven design allows linear motion companies to validate product claims against ISO 14728 standards.
5. Key Factors Affecting Linear Guide Lifespan
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan | Optimization Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Material & Heat Treatment | Hardness and fatigue resistance | Use high-quality bearing steel with proper quenching |
| Slider Design | Roller guides handle higher loads | Choose DB/DF structure based on application |
| Lubrication | Poor lubrication accelerates wear | Automatic or periodic lubrication recommended |
| Installation Accuracy | Misalignment reduces lifespan | Ensure parallelism and correct pre-load |
| Environment | Dust, corrosion, or high humidity | Protective coatings or covers |
Considering these factors allows linear motion companies to optimize guide selection and extend service life.
Advantages of DTX-LG Linear Guides
DTX-LG linear guides are designed with ISO 14728 in mind:
- High load capacity tested for L10 lifespan
- Precision-ground rails and low clearance for stable linear motion
- Corrosion-resistant coatings for long-term reliability
These features make DTX-LG an ideal choice for Robot Manufacturers, End-User Manufacturers, Linear Motion Module Manufacturers seeking reliable, high-performance linear guides compatible with Hiwin, Bosch Rexroth, and other leading brands.
Conclusion
Accurate lifespan calculation is critical for linear motion companies, linear rail companies, and linear guide manufacturers. ISO 14728 provides a trusted framework to predict linear guide reliability under real-world conditions.
By following theory, applying practical calculation steps, and considering operational factors, engineers can ensure long-lasting, high-performance linear guides. Choosing high-quality products like DTX-LG ensures system precision, reduces maintenance, and demonstrates the expertise of a professional linear motion company.
