-
01/15/2026
- 0 Comment
Vertical VS Horizontal Linear Guide Selection
Table of Contents
In the world of linear motion system, one seemingly simple choice can actually make or break your equipment: picking the right linear guide for horizontal (Y-axis) and vertical (Z-axis) movement.
It’s not just about choosing a direction. Pick the wrong guide, and you could end up with unstable precision, shortened lifespan, or worse—safety risks and serious financial losses. In this article, we’ll break down the key differences between Y-axis and Z-axis linear guides and give you a straightforward framework to help you select the right one, building a rock-solid motion core for your machines.
definition of Vertical & Horizontal Linear guide
What is horizontal linear guide?
A horizontal linear guideway typically refers to a guideway system along the X and Y axes that drives the load to move precisely in a horizontal direction (front, back, left, and right). It is the cornerstone of the horizontal movement of a worktable or slide. Experience less gravitational load in the motion direction. Gravity may still affect the guide perpendicularly but does not significantly increase axial load. Horizontal guides are widely used in:
- Precision XY tables
- Conveyors and pick-and-place machines
- Robotic arms with predominantly horizontal motion
Horizontal applications face challenges such as moment loads, cantilever effects, and maintaining accuracy over long travel distances, but the gravitational load in the motion direction is typically much smaller than for vertical guides.
What is vertical linear guide?
Vertical linear guides refer to z are commonly used in Z Axis linear Guideway applications such as CNC milling machines, 3D printers, and lifting mechanisms. These guides must support the weight of moving components while maintaining accuracy and repeatability. Vertical orientation introduces axial load due to gravity, which can cause several challenges:
- Downward drift or slippage under heavy loads
- Increased wear on bearing surfaces
- Sensitivity to pre-load and installation accuracy
- Potential vibration or backlash if the guide is not sufficiently rigid
For these reasons, vertical guides require careful attention to load capacity, structural rigidity, and friction management.
Linear Guide Types
Choosing the optimal linear guide for linear motion in different directions also depends on understanding the mechanical structure and performance advantages of different guide types.

Ball Type Linear Guides
Ball-type linear guides are the most common solution, renowned for their high precision, low friction, and smooth motion. Featuring high-speed capability and excellent repeatability, they are well-suited for light to medium load applications and are frequently employed in the 3 axes linear guide systems of CNC machines for X and Y-axis movement. To enhance performance, some models incorporate multiple rows of balls (2-4 rows), which significantly improves system rigidity. However, in vertical (Z-axis) applications under heavy loads—common in vertical CNC machining centers—ball guides may be prone to slippage or uneven wear, often necessitating pre-load adjustment or high-rigidity designs to ensure stability. From a cost perspective, they are generally the most cost-effective option for such multi-axis systems due to relatively simpler manufacturing processes and lighter material requirements.
Roller Type Linear Guides
Roller guide rails assembly utilize cylindrical rollers in place of balls, which significantly increases the contact surface area between the components. As a result, they offer a substantially higher load capacity—often two to three times that of similarly sized ball guides—and provide excellent rigidity. This makes them particularly suitable for applications involving heavy vertical (Z-axis) or cantilevered loads, such as serving as the robust CNC Z axis linear guide in machining centers. While the design leads to slightly higher friction, rendering them ideal for moderate-speed operations, their core strength lies in environments demanding extreme rigidity and durability, which is critical for the precision and stability of a CNC machine’s Z-axis. In terms of cost, roller guides are typically the most expensive among common linear guide types due to their more complex components and greater material usage.
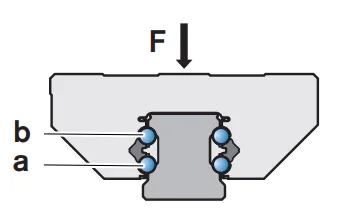
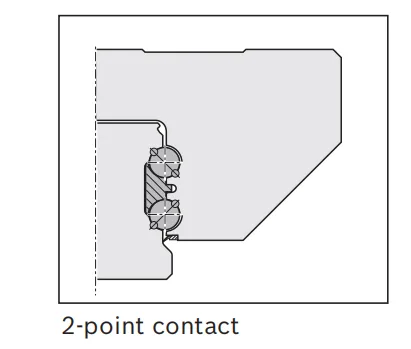
DB Structure Linear Guides
Double-row Ball Carriage DB compact linear rail guides represent a hybrid solution that strategically positions rolling elements along the rail’s mid-section. This unique design significantly enhances torque resistance and load-handling capability, particularly in vertical (Z-axis) or high-load applications. By utilizing four rows of balls that maintain two points of contact in all loading directions, DB guides deliver superior rigidity compared to standard ball guides while reducing the differential sliding friction common in traditional multi-row designs. This makes them a cost-effective alternative to roller guides for scenarios involving medium to heavy loads or cantilevered structures. In terms of cost, DB guides occupy a middle ground—more affordable than roller guides yet offering a favorable balance of enhanced rigidity, improved load capacity, and reduced operational friction.
Summary of Cost Ranking:
Ball linear guide < DB linear guide < Roller linear guide
This ranking reflects typical manufacturing complexity and material requirements for each type. Designers should weigh the cost against load, precision, and application demands.
Vertical linear guideway vs Horizontal linear guideway
Application of both linear guide
| Factor | Vertical Guide | Horizontal Guide |
|---|---|---|
| Load Direction | Axial + Gravity | Mainly Radial |
| Ball Guide | Light loads only; may slip under heavy weight | High-speed, precise motion, long life |
| Roller Guide | Optimal for high vertical loads and rigidity | Heavy loads; moderate speed |
| DB Structure | High rigidity and torque resistance; suitable alternative to roller | Optional; increases rigidity if needed |
| Friction Management | Critical to minimize | Important but less critical |
| Cost Ranking | DB < Roller; Ball for light loads | Ball < DB < Roller |
Vertical applications demand high rigidity, friction management, and careful load distribution, while horizontal applications provide more flexibility in guide choice.
Selection of both linear guide
Selecting the right linear motion system requires a strategic balance of load, orientation, precision, speed, and cost. For vertical (Z-axis) applications, DB structure guides offer an excellent compromise of load capacity and rigidity for medium-duty use, while roller guides are the premier choice for extreme loads demanding maximum rigidity. Ball guides can suffice for light vertical loads where speed and precision are paramount, provided measures like pre-load adjustment are implemented. In horizontal applications, ball guides excel for high-speed, high-precision motion, whereas roller guides are preferred for handling heavy horizontal loads. DB guides serve as a versatile middle-ground option in either orientation, providing enhanced rigidity over standard ball guides without the full cost of roller guides. Key additional considerations include: opting for roller or DB guides for long travel distances to maintain alignment, favoring low-friction ball guides for high dynamic loads, and aligning the choice with budget—where ball guides are most cost-effective, DB structures offer a balanced upgrade, and roller guides justify their higher cost in the most demanding high-load scenarios.
Common Mistakes
- Using standard ball guides for heavy vertical Z-axis loads → can cause slippage or increased backlash
- Using low-capacity DB guides for heavy horizontal loads → may increase pre-load friction
- Neglecting installation precision → even DB or roller guides can develop side-play if mounted incorrectly
There is no single “best” guide type; selection depends on orientation, load, precision, and cost considerations:
Vertical applications: DB or roller guides generally outperform ball guides in heavy-load and torque-critical scenarios
Horizontal applications: Ball guides are cost-effective for light loads, while roller or DB guides are suitable for heavier loads or applications needing high rigidity
Cost Perspective: Ball < DB < Roller. Designers should balance cost vs. performance based on load, orientation, and precision requirements.
DTX-LG as a linear rail company provides a complete series of linear guides (ball, roller, DB) for vertical and horizontal applications, ensuring precision, stability, and long service life. Our engineers can assist in selecting the most cost-effective and application-specific guide solution, optimizing performance while minimizing unnecessary expenses.